Additive vs Subtractive Manufacturing
Many manufacturing processes have adopted the inclusion of digital elements. This rise of digital methods throughout manufacturing is part of a broader movement to create a more accurate, efficient and cost-effective approach that increases a company's competitiveness within its field.
CNC machines and smart factories are excellent examples of how digitisation can positively improve manufacturing processes, but this is only the beginning, as other innovations are implemented. The digital revolution is a vital part of the manufacturing industry's future and has led to the creation of many superior processes, including prototype manufacturing.
Additive and subtractive are both effective processes but very different in their approaches. However, despite their differences, there are significant overlaps in their applications, usually resulting in both these processes being used sequentially. For example, additive manufacturing is quite often used before subtractive during the prototyping stage.
What Is Additive Manufacturing?
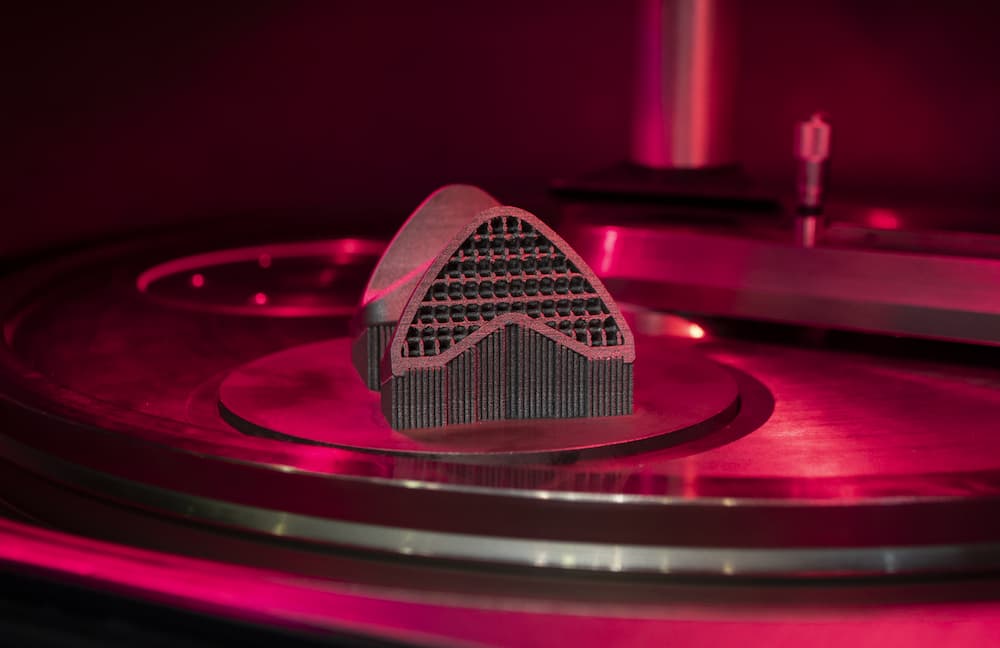
Additive manufacturing is a process that many people are familiar with but unaware of what it's called. The term that most people know is 3D printing. 3D printing fits this manufacturing category, as the concept is to build an object out of raw materials, essentially adding material to it until complete. This process relies on CAD (computer-aided design) in order to dictate the design of the component created through this additive process.
The term additive relates to the various technologies that can seemingly grow a 3D object by adding one superfine layer at a time. These layers are dictated by the CAD design, which has been sliced into delicate layers. Each of these layers will bond with the previous as they are applied.
Additive Manufacturing Applications
At Dean Group, we specialise in providing a superior rapid casting prototyping service with our high-end 3D printing units. This process has been a significant improvement over traditional methods for many reasons, the main one being improved lead times.
The application of additive manufacturing is widely embraced in many sectors such as aerospace, defence and medical to achieve more accurate and cost-effective results than previous methods. However, the required units will factor in choosing additive over subtractive manufacturing for your final production. Additive manufacturing is commonly used for the early stages of development and smaller manufacturing runs.
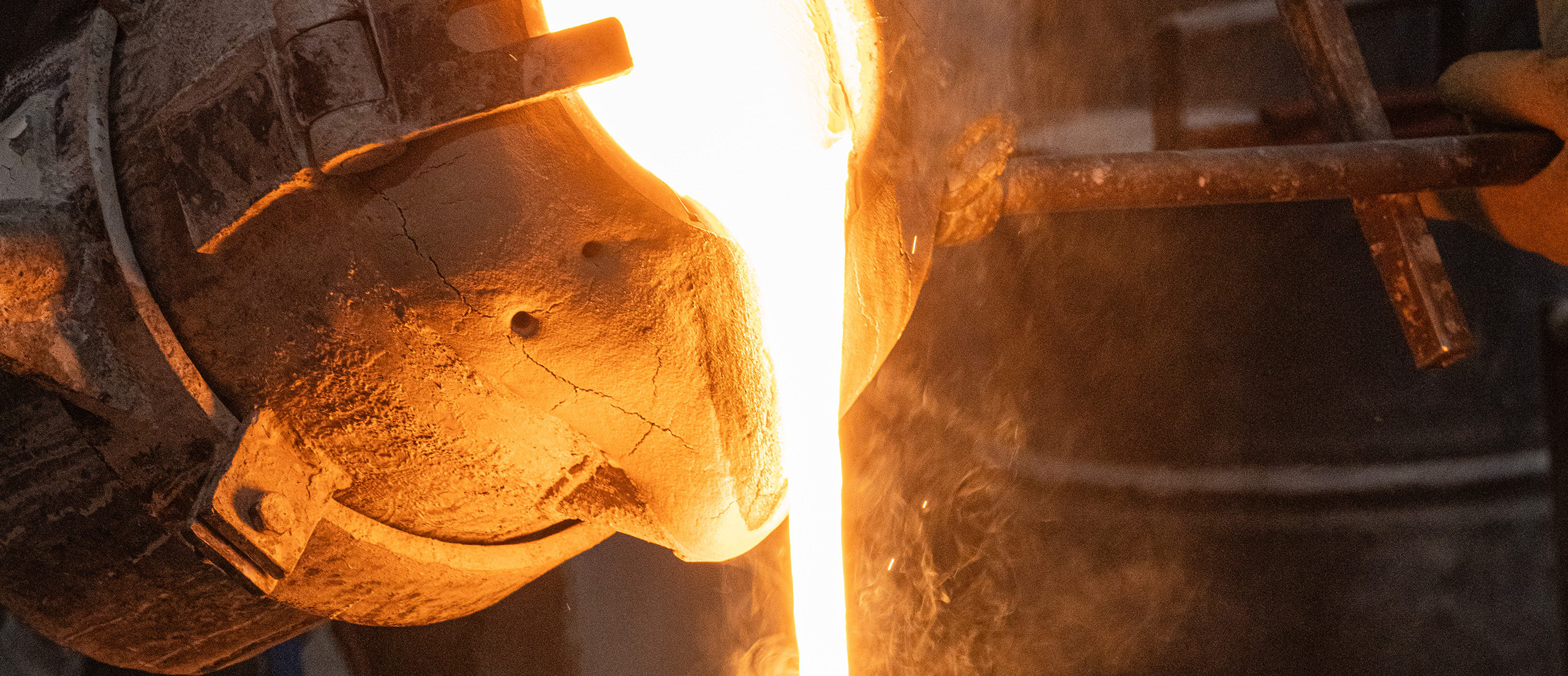
Additive Manufacturing for Investment Casting
Additive manufacturing has many benefits over alternatives, especially in the early stages of development, such as investment casting. When the design is not locked yet, these exploratory stages can be extensive processes of creation, feedback and re-creation to find the perfect design.
Additive manufacturing is an excellent choice for product development, but it’s also been used with subtractive manufacturing to create complex components such as jewellery production, robotic and electromechanical systems and medical applications.
Our UK-based casting foundry offers lost wax castings via a 3d wax printer route that enable you to observe your physical prototype with much shorter lead times, thanks to our Thermojet wax modelling system. This additive manufacturing method allows you to choose a locked design sooner and consider moving ahead with more durable materials. Once the design has been locked thanks to an effective prototype made in additive manufacturing, it's common for more companies to choose subtractive manufacturing to fulfil their larger orders.
What Is Subtractive Manufacturing?
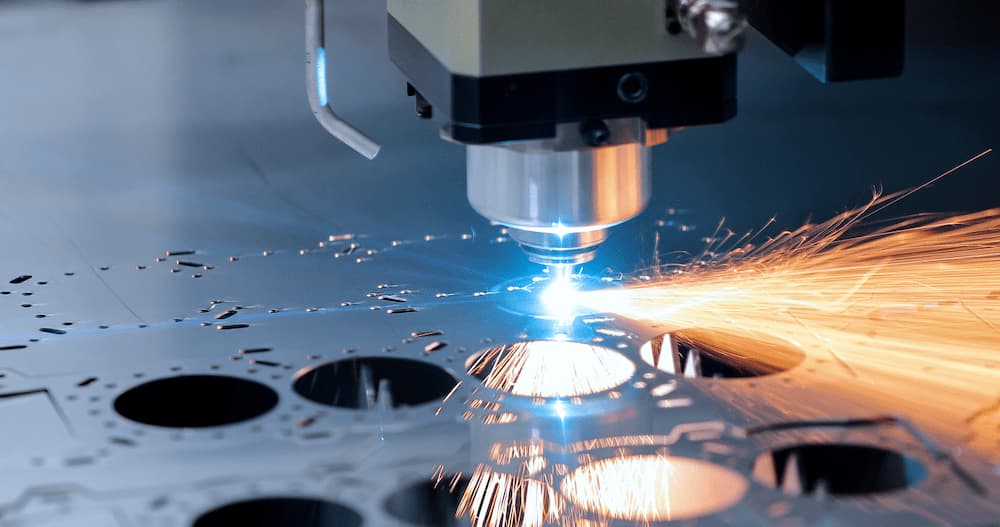
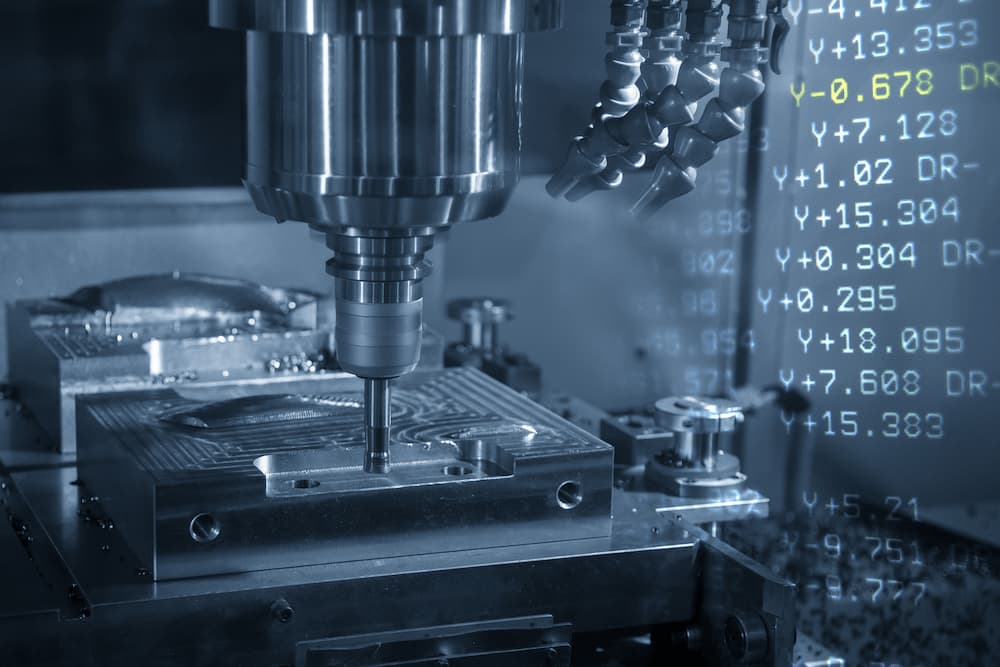
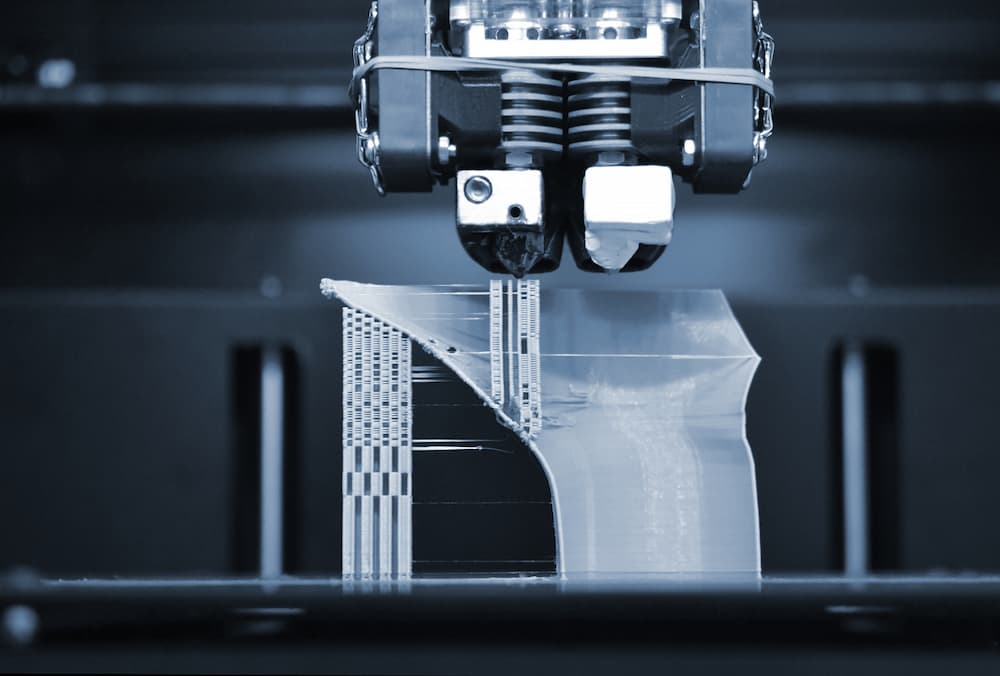
Subtractive manufacturing is a broad term that applies to many different manufacturing processes. This is a more conventional method of manufacturing in that it relies upon removing unwanted material and leaving only your desired design behind. This works in relation to many other material removal processes, such as cutting, pressing, and grinding. These processes used to be performed manually at slower rates, but with digital methods such as CNC machining, subtractive manufacturing has become a standard across the industry due to the improved working speed, fidelity and reduced costs.
Subtractive Manufacturing Applications
The number of applications for subtractive manufacturing is endless; in essence, subtractive manufacturing is the concept of cutting away raw materials to get your final product, such as drilling and cutting. This classic form of manufacturing can be used for many projects at any stage, from prototyping to final production. The issue with subtractive manufacturing that puts it behind the additive alternative is the produced waste.
Because subtraction relies on removing excess raw material, it inherently creates waste that must be disposed of. This is a significant drop in material efficiency is why subtractive manufacturing is usually saved until you have your design locked through additive manufacturing prototyping. This way, you can limit the waste of your later, subtractive process to minimal levels with an efficient design that isn't going to change.
Subtractive manufacturing processes are ideal for large batch production of components. Additionally, It’s the best choice for pieces with a contoured profile and textured surface fabrication.
In summary, both additive and subtractive manufacturing methods are excellent processes that enable manufacturers to create any components. But when used in conjunction, they would allow designers to fulfil their visions faster than older methods.
At Dean Group, we specialise in providing an effective prototyping process to ensure our clients can get what they need in minimal time. Contact us directly to discuss which strategy best suits your business's needs.
Registered in England VAT No: 146307478 Company Registration No: 1062820